Elasticsearch¶
This extension allows to integrate Foliant-managed documentation projects with Elasticsearch search engine.
The main part of this extension is a preprocessor that prepares data for a search index.
Also this extension provides a simple working example of a client-side Web application that may be used to perform searching. By editing HTML, CSS and JS code you may customize it according to your needs.
Installation¶
To install the preprocessor, run the command:
$ pip install foliantcontrib.elasticsearch
To use an example of a client-side Web application for searching, download these HTML, CSS, and JS files and open the file index.html in your Web browser.
Config¶
To enable the preprocessor, add elasticsearch to preprocessors section in the project config:
preprocessors:
- elasticsearch
The preprocessor has a number of options with the following default values:
preprocessors:
- elasticsearch:
es_url: 'http://127.0.0.1:9200/'
index_name: ''
index_copy_name: ''
index_properties: {}
actions:
- delete
- create
use_chapters: true
format: plaintext
escape_html: true
url_transform:
- '\/?index\.md$': '/'
- '\.md$': '/'
- '^([^\/]+)': '/\g<1>'
require_env: false
targets: []
es_url- Elasticsearch API URL.
index_name- Name of the index. Your index must have an explicitly specified name, otherwise (by default) API URL will be invalid.
index_copy_name- Name of the index copy when the
copyaction is used; see below. If theindex_copy_nameis not set explicitly, and if theindex_nameis specified, theindex_copy_namevalue will be formed as theindex_namevalue with the_copystring appended to the end. index_properties- Settings and other properties that should be used when creating an index. If not specified (by default), the default Elasticsearch settings will be used. More details are described below.
actions-
Sequence of actions that the preprocessor should to perform. Available item values are:
delete,create,copy. By default, the actionsdeleteandcreateare performed since in most cases it’s needed to remove and then fully rebuild the index. Thecopyaction is used to duplicate an index, i.e to create a copy of the indexindex_namewith the nameindex_copy_name. This action may be useful when a common search index is created for multiple Foliant projects, and the index may remain incomplete during for a long time during their building. Thecopyaction is not atomic. To perform it, the preprocessor:- marks the source index
index_nameas read-only; - deletes the target index
index_copy_nameif it exists; - clones the source index
index_nameand thereby creates the target indexindex_copy_name; - unmarks the source index
index_nameas read-only; - also unmarks the target index
index_copy_nameas read-only, since the target index inherits the settings of the source one.
- marks the source index
use_chapters- If set to
true(by default), the preprocessor applies only to the files that are mentioned in thechapterssection of the project config. Otherwise, the preprocessor applies to all of the files of the project. format- Format that the source Markdown content should be converted to before adding to the index; available values are:
plaintext(by default),html,markdown(for no conversion). escape_html- If set to
true(by default), HTML syntax constructions in the content converted toplaintextwill be escaped by replacing&with&,<with<,>with>, and"with". url_transform- Sequence of rules to transform local paths of source Markdown files into URLs of target pages. Each rule should be a dictionary. Its data is passed to the
re.sub()method: key as thepatternargument, and value as thereplargument. The local path (possibly previously transformed) to the source Markdown file relative to the temporary working directory is passed as thestringargument. The default value of theurl_transformoption is designed to be used to build static websites with MkDocs backend. require_env- If set to
true, theFOLIANT_ELASTICSEARCHenvironment variable must be set to allow the preprocessor to perform any operations with Elasticsearch index. This flag may be useful in CI/CD jobs. targets- Allowed targets for the preprocessor. If not specified (by default), the preprocessor applies to all targets.
Usage¶
The preprocessor reads each source Markdown file and generates three fields for indexing:
url—target page URL;title—document title, it’s taken from the first heading of source Markdown content;content—source Markdown content, optionally converted into plain text or HTML.
When all the files are processed, the preprocessor calls Elasticsearch API to create the index.
Optionally the preprocessor may call Elasticsearch API to delete previously created index.
By using the index_properties option, you may override the default Elasticsearch settings when creating an index. Below is an example of JSON-formatted value of the index_properties option to create an index with Russian morphology analysis:
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"filter": {
"ru_stop": {
"type": "stop",
"stopwords": "_russian_"
},
"ru_stemmer": {
"type": "stemmer",
"language": "russian"
}
},
"analyzer": {
"default": {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
"ru_stop",
"ru_stemmer"
]
}
}
}
}
}
You may perform custom search requests to Elasticsearch API.
The simple client-side Web application example that is provided as a part of this extension, performs requests like this:
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "foliant",
"type": "phrase_prefix",
"fields": [ "title^3", "content" ]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"content": {}
}
},
"size": 50
}
Search results may look like that:
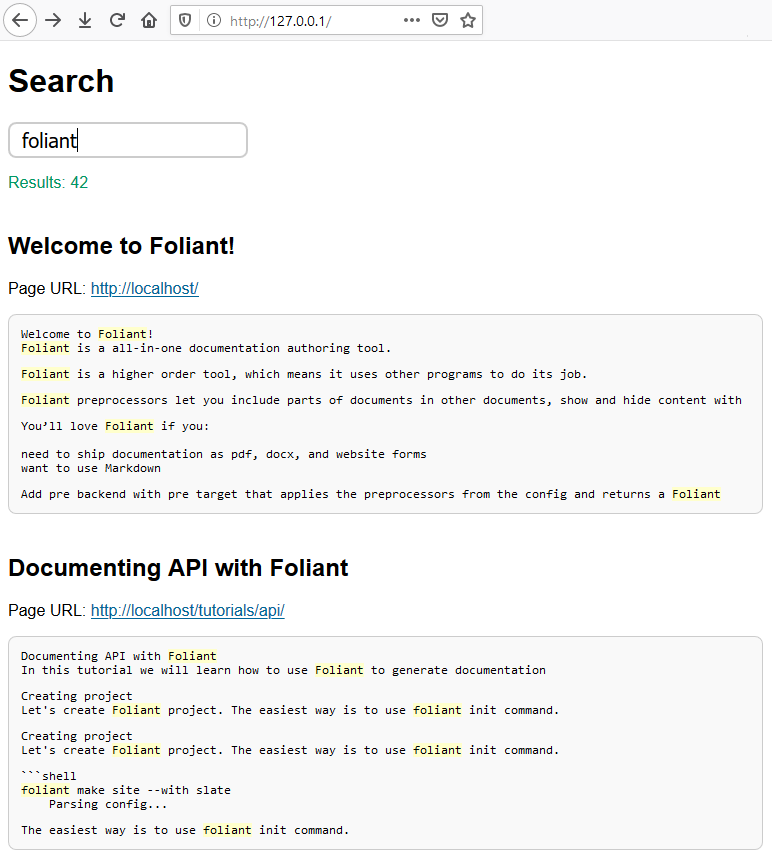
If you use self-hosted instance of Elasticsearch, you may need to configure it to append CORS headers to HTTP API responses.